The global prevalence of overweight and obese children, including in Vietnam, is increasing rapidly. Excess weight increases the risk of developing conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and other chronic illnesses. Overweight and obese children require a scientifically balanced diet to reduce excess fat while ensuring proper nutrition for their comprehensive development.

1. Causes of Overweight and Obesity
- Dietary Habits: Overconsumption of fatty and sugary foods, eating when not hungry, or eating while watching TV or engaging in other activities.
- Genetic Factors: Obesity often has a clear genetic component within families, although endocrine disorders and genetics play a minor role in childhood obesity.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Insufficient exercise and physical activity.
- Medication: Obesity can result from the side effects of medications or endocrine disorders that disrupt regular fat storage in the body. However, this is a less common cause.
- Other Factors: Low birth weight and inadequate sleep can also contribute to childhood obesity.
2. What to Do for Overweight and Obese Children
- Maintain a balanced and varied diet for children, avoiding excessive consumption of specific food types.
- For those who consume milk, choose unsweetened options, and older children should opt for skim milk (skimmed milk powder). Avoid sweetened condensed milk.
- Have regular, balanced meals, and do not skip meals. Avoid letting children become too hungry because when they are, they tend to overeat at subsequent meals.
- Food Preparation: Minimize fried or sautéed dishes; opt for steamed, boiled, or baked alternatives.
- Encourage thorough chewing and slow eating (rapid eating may lead to overconsumption), each meal lasting around 30 minutes.
- Ensure that children have a substantial breakfast to prevent snacking at school and reduce consumption during the afternoon and evening.
- Include more vegetables and fewer sweet fruits in the diet. Replace some rice with potatoes, corn, or other high-fiber foods. Choose whole grains or low-fat bread.
- Families should eat together, making mealtime a relaxed, shared moment for discussing the day’s events.
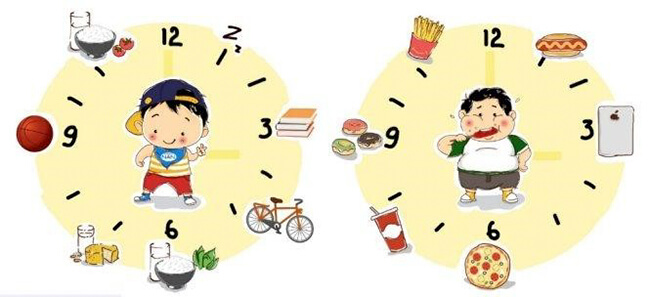
3. What Not to Do for Overweight and Obese Children
- Avoid giving children sugary sodas or carbonated beverages.
- Limit the consumption of candies, honey, ice cream, condensed milk, and sweets with added sugar.
- Refrain from storing energy-dense foods like butter, cheese, cakes, candies, chocolates, ice cream, and sugary drinks in the house.
- Do not feed children shortly before bedtime.
- Discourage children from chewing gum regularly, which may encourage constant snacking.
- Avoid overloading children with excessive academic work. Provide opportunities for them to engage in recreational activities to relieve stress and be physically active.
4. Measures to Increase Physical Activity
- Parents should support and facilitate physical activity for children.
- Foster children’s enthusiasm for sports and physical activities.
- Focus on integrating sports and physical activities into daily life, such as walking to school, running, skipping, playing soccer, badminton, volleyball, or climbing stairs.
- Involve children in household chores like cleaning, carrying water, and lifting objects.
- Ensure children drink enough water to replace fluids lost during exercise.
- Limit sedentary activities such as watching TV, videos, and electronic games.
- Promote regular physical activities for children while adjusting their diet sensibly to achieve and maintain a healthy weight and overall well-being.


