1. How is Breast Milk Produced?
- The breast is composed of glandular tissue, ducts, and supportive muscles. Its function is to produce, synthesize, and transport milk to the nipple.
- The amount of breast tissue varies among women. Breast size is not related to milk production capacity.
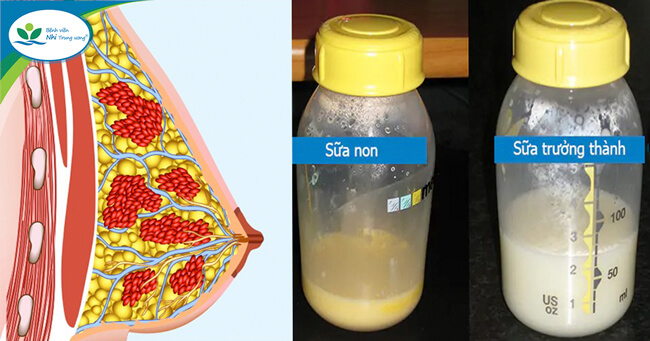
- Around halfway through pregnancy, colostrum begins to be produced until 36-96 hours after birth, appearing yellow and providing sufficient quantity for newborns. The high nutritional and immune content of colostrum makes it perfect for newborns.
- Colostrum gradually transitions into transitional milk 36-96 hours after birth, becoming mature milk after 9-30 days.
2. Benefits of Breast Milk
Breast milk contains various vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Every 100ml of breast milk can provide 60-75 kcal. Additionally, breast milk contains immune factors beneficial for infants such as white blood cells, IgA, IgM, growth factors, and other antibacterial agents.
Benefits of breast milk:
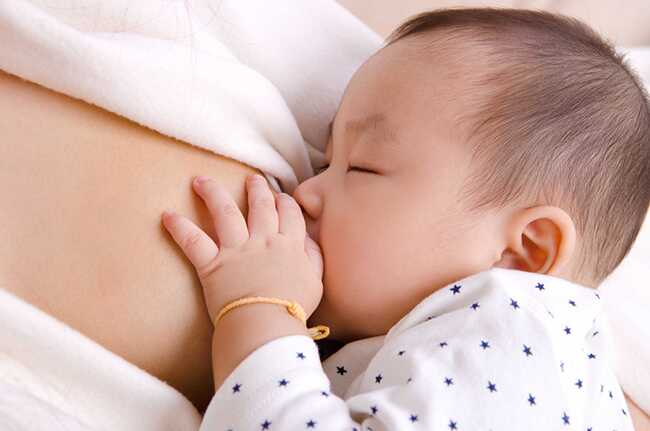
- Nursing with breast milk enhances the mother-child bond through cuddling, breastfeeding, skin-to-skin contact during feeding, and eye contact, aiding in the child’s emotional development.
- Breastfed infants are at lower risk of diseases such as obesity, digestive disorders, and blood sugar disorders.
- Breastfed infants are less likely to contract infections such as neonatal infections and gastrointestinal infections.
- Breast milk promotes comprehensive development, providing essential fats, proteins, vitamins, and DHA for healthy and intelligent development.
- Breastfeeding is the most economical method of feeding.
- Nursing with breast milk aids in quicker postpartum recovery for mothers, facilitating faster uterine involution, reducing postpartum fluid, blood loss, postpartum infection rates, and quicker postpartum endocrine balance.
- Breastfeeding reduces the risk of breast cancer and ovarian cancer in women.

3. Risks of Improper Breast Milk Usage
- Children may contract some diseases transmitted through breast milk. Therefore, mothers should not feed their children milk from unknown sources or from individuals whose health status is uncertain.
- Risk of infection: improperly stored and used expressed breast milk is susceptible to contamination. If a child consumes contaminated milk, the risk of gastrointestinal infections is high. Therefore, it is recommended that mothers breastfeed directly rather than expressing milk.
4. How to Maintain Breast Milk Supply
- Initiate breastfeeding early to stimulate milk production.
- Ensure correct positioning and latch-on.
- Support proper oxytocin reflex activity.
- Ensure frequency and duration of breastfeeding.
- Express milk regularly, and express residual milk after feeding to increase milk production.
- Mothers should have adequate rest and moderate, sensible physical activity.
- Nutrition: Mothers should have a balanced, nutritious diet, consume plenty of fruits and vegetables, drink enough water, avoid alcohol, and avoid foods that may alter the taste of breast milk.
- Only use medications when prescribed by a doctor.
- Avoid contraceptive pills containing estrogen as they may affect milk production.
5. Cách bảo quản sữa mẹ
| Room Temperature 19-26°C | Refrigerator | Freezer (-20°C) | |
| Freshly Expressed Breast Milk |
• LIdeally used immediately after expression • ≤ 6 hours at room temperature |
≤ 5 days in the refrigerator |
≤ 6 months in the freezer
|
| Previously Frozen Milk, Thawed in the Refrigerator but Not Heated |
≤ 4 hours |
≤ 24 hours | Do not refreeze |
| Previously Frozen and Thawed at Room Temperature |
Use immediately |
≤ 4 hours | Do not refreeze |
| Pasteurized Breast Milk (after slow thawing from the refrigerator) |
≤ 4 hours |
≤ 48 hours | Do not refreeze |
6. How to Use Refrigerated Breast Milk
Method 1: Allow the milk to sit at room temperature for 30-45 minutes.
Method 2: Warm in warm water at 37°C if immediate use is required.
***Note:
- Do not heat breast milk, do not microwave.
- Breast milk should be stored separately, not mixed with other foods.
- Leftover milk that the baby has already consumed should not be saved.
Neonatal Center
Vietnam National Children’s Hospital



